From love to a person, from respect to nature.
Diamonds? Diamonds..
Lab-grown diamonds, often referred to as lab-created diamonds, man-made diamonds, engineered diamonds, or cultured diamonds, are cultivated within meticulously controlled laboratory settings. These environments replicate the conditions found deep beneath the Earth's crust where natural diamonds take shape. Lab-created diamonds are constructed from genuine carbon atoms, mirroring the distinctive crystal structure of natural diamonds. As a result, they share identical optical and chemical properties with their natural counterparts.

How are lab-diamonds made?
The Production of Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds originate from minute carbon seeds sourced from existing diamonds. Utilizing cutting-edge technology, scientists replicate the natural diamond formation process, employing either extreme pressure and heat or a specialized deposition technique known as chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Over a span of six to ten weeks, a raw diamond emerges, which is subsequently meticulously cut, polished, and integrated into lab-grown diamond jewelry items like earrings, necklaces, or bracelets.
Two primary methods are employed for lab diamond fabrication:
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT): This method emulates the geological conditions in which natural diamonds evolve beneath the Earth's surface. To produce a lab diamond using HPHT, a substantial machine is supplied with a specific quantity of carbon material, subjecting it to crushing pressures exceeding 870,000 pounds per square inch and extreme temperatures ranging from 1300 to 1600 degrees Celsius.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): CVD entails placing a seed diamond within a compact vacuum chamber filled with heated hydrogen and carbon-rich gases. At a particular temperature, gas molecules disintegrate, instigating the formation of carbon layers around the seed, resulting in the growth of a larger diamond. Some lab diamonds created through the CVD method may undergo additional pressure and heat treatment post-growth.
Distinguishing between natural diamonds, lab diamonds produced via the HPHT method, and lab diamonds cultivated through CVD is imperceptible to the naked eye; only scientists can differentiate them by analyzing identifying markers arising from the growth conditions.
CUT | AGS 000
Triple Zero or AGS 000 is a term used to describe the highest possible cut grade for diamonds, signifying perfection in three key aspects: proportions, symmetry, and polish. To achieve this exceptional rating, a diamond must exhibit ideal proportions (0), flawless polish (0), and impeccable symmetry (0). This triple-zero grade represents a rare combination of excellence in these crucial areas.
The AGS Angular Spectrum Evaluation Tool (ASET) stands as the sole diamond cut grading tool endorsed by the scientific community. ASET utilizes a color-coded map to illustrate how light interacts with a diamond. These ASET Maps are invaluable for evaluating a diamond's brightness, contrast, and the presence or absence of light leakage.

Conflict-free and environmentally friendly
Lab-grown diamonds embody a beautiful convergence of values, transcending the realm of emotions and ethics. They represent our love for the special people in our lives and our deep respect for the natural world that sustains us.
In choosing lab-grown diamonds to celebrate moments of love and commitment, we send a powerful message. These gems, crafted with precision and care in controlled laboratory environments, symbolize our affection for our loved ones. They are not only exquisite and conflict-free but also a testament to our commitment to the responsible stewardship of our planet.
By opting for lab-grown diamonds, we bridge the gap between the personal and the ecological, ensuring that the tokens of our affection align with our respect for nature. With every lab-grown diamond, we affirm our love for our partners, our families, and our planet—a harmonious blend of sentiment and sustainability.

IGI certification
The International Gemological Institute (IGI) is one of the world's most renowned and respected gemological laboratories, specializing in the certification of diamonds and other gemstones. IGI certification is highly regarded within the jewelry industry and among consumers seeking reliable information about their gemstone purchases, particularly diamonds. Here are some key points about IGI certification:
Accurate Grading: IGI employs a team of highly trained gemologists who meticulously assess and grade diamonds based on the well-established "Four Cs" criteria: Carat weight, Cut quality, Color grade, and Clarity grade. Their assessments are recognized for their precision and consistency.
Detailed Documentation: An IGI diamond certificate provides comprehensive details about the diamond's characteristics, including its shape, measurements, weight, cut grade, color grade, clarity grade, and more. This documentation is a valuable resource for both jewelers and consumers, aiding in transparency and informed decision-making.
Laser Inscription: Many IGI-certified diamonds feature a microscopic laser inscription on the girdle of the stone. This inscription typically includes the certificate number, making it easier to match the diamond to its corresponding certificate and enhancing security against fraud.
International Recognition: IGI is an internationally recognized gemological institute with laboratories and offices across the globe. Its certificates are respected and acknowledged worldwide, facilitating trade and ensuring consumer confidence.
Treatment Disclosure: IGI certification includes information about any treatments or enhancements that may have been applied to the diamond. This transparency is essential for buyers to understand the true nature of the gemstone they are purchasing.
Appraisal and Authentication: Beyond certification, IGI can also provide appraisal services to determine the market value of a diamond. This service is often utilized for insurance purposes and estate planning.
Ongoing Research: IGI is committed to ongoing research and innovation in gemology. They continuously improve their grading standards and stay at the forefront of developments in the diamond industry.
When purchasing a diamond, especially one of significant value, obtaining an IGI certificate is a valuable step to ensure you are receiving a genuine and accurately graded gemstone. It provides peace of mind, authenticity, and a basis for fair pricing in the diamond market.
4C
The "4Cs" in the diamond industry refer to the four key characteristics used to assess and determine the quality of a diamond. These characteristics are:
-
Carat Weight: Carat weight measures the size of the diamond. It's important because larger diamonds are generally rarer and can be more valuable.
-
Cut Quality: Cut quality assesses how well a diamond has been shaped and faceted. It's crucial because a well-cut diamond reflects light beautifully and appears more brilliant.
-
Color Grade: Color grade evaluates the presence of color in a diamond. It's significant because diamonds with less color (closer to colorless) are considered more valuable.
-
Clarity Grade: Clarity grade examines the presence of internal or external imperfections in a diamond. It's important because diamonds with fewer imperfections are typically more valuable.
The 4Cs are highly important because they collectively determine a diamond's quality, beauty, and value. The combination of these characteristics influences how the diamond looks, sparkles, and is priced. Buyers use the 4Cs to make informed choices and select diamonds that match their preferences and budget. Diamond professionals use them to grade and price diamonds accurately.

Carat Weight
Carat weight is the measure of a diamond's size and is one of the most easily noticeable factors. One carat is equivalent to 0.2 grams, and diamonds are often measured in points, with one carat equaling 100 points. Larger diamonds are generally rarer and more valuable, but the value can vary significantly based on the other 3Cs.
Cut Quality
The cut of a diamond refers to how well it has been shaped and faceted, which directly impacts its sparkle and brilliance. Cut quality includes several aspects:
Proportions: The proportions of a diamond determine how light interacts with it. Well-proportioned diamonds reflect light effectively, resulting in a bright and beautiful appearance.
Symmetry: Symmetry involves the alignment of facets and how well they mirror each other. Precise symmetry enhances a diamond's sparkle.
Polish: Polish refers to the smoothness and quality of the diamond's surface. A well-polished diamond exhibits excellent light reflection.
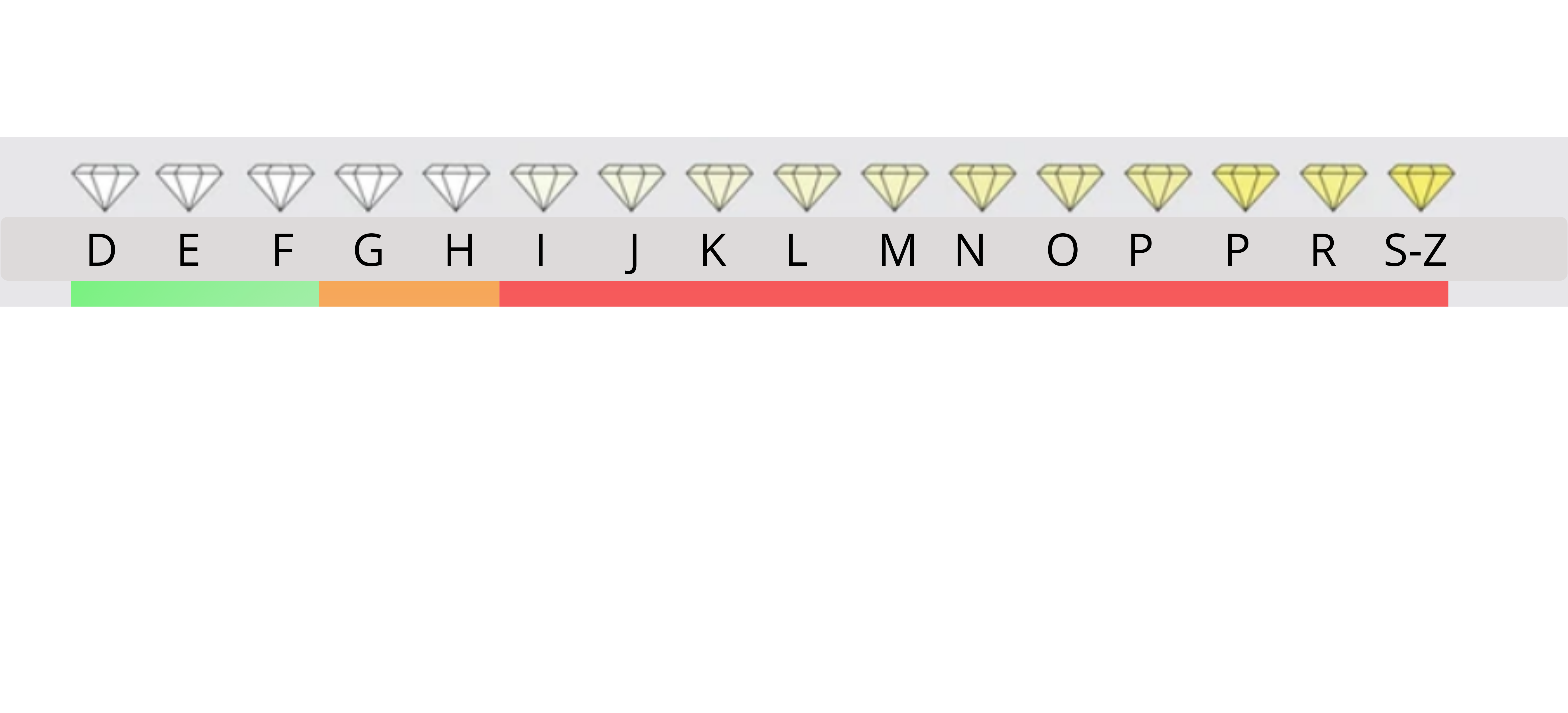
Color Grade
The color grade of a diamond assesses its lack of color. Diamonds are graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). The less color a diamond exhibits, the more valuable it is, with D being the most desirable.
Clarity Grade
Clarity evaluates the presence of internal and external imperfections or inclusions in the diamond. These natural characteristics are like the diamond's birthmarks and are assessed on a scale that ranges from Flawless (no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification) to Included (inclusions and/or blemishes visible to the naked eye). Higher clarity grades indicate greater rarity and value.